Bits, Bytes & Vision
Exploring the intersection of high performance computing, modern C++, computer vision, and storage systems. Deep technical insights into building performant software systems, optimizing databases, and implementing efficient computer vision algorithms.
Project maintained by sam-herman Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
Teaching Embedding Models New Words: A Deep Dive into Domain Adaptation
Reading Time: ~25 minutes
TL;DR: I spent weeks trying to make an embedding model understand a made-up word. What I learned along the way reveals why “just fine-tune it” is terrible advice for domain-specific search, and what actually works.
The Problem That Started This Journey
Neural embedding models have revolutionized information retrieval, yet their practical deployment in enterprise environments remains challenging. While these models excel on benchmark datasets, they consistently underperform on domain-specific corpora containing specialized terminology, acronyms, and jargon absent from their pre-training vocabulary.
This investigation started with a simple question: Can I teach a pre-trained embedding model to recognize and semantically reason about entirely novel vocabulary?
Through controlled experimentation with the SPLADE architecture, I discovered that naive fine-tuning approaches fail to achieve meaningful domain adaptation. The root cause—insufficient MLM (Masked Language Modeling) logit activation for out-of-vocabulary terms—led me down a rabbit hole that ultimately produced a multi-stage adaptation pipeline that actually works.
What I’ll cover:
- Why standard fine-tuning fails for domain vocabulary adaptation
- A diagnostic framework for identifying vocabulary integration failures at the MLM logit level
- A staged adaptation methodology combining vocabulary extension, domain warmup pre-training, dictionary-based pre-training, and multi-objective fine-tuning
- How to achieve successful semantic query expansion to novel domain terminology
Introduction
The Domain Adaptation Challenge
At OpenSearchCon 2025 NA, I challenged a common misconception in the vector search space: that the index is the primary driver of good recall. Marketing teams and vendors love to focus on index architecture, but my research pointed to a different culprit. The main factor degrading recall and search relevancy in production isn’t the index—it’s the quality of the embeddings themselves.
To put this in perspective: a typical ANN index (HNSW, IVF, etc.) achieves 95-99% recall relative to exact k-NN search. That’s a 1-5% loss from approximate indexing. Meanwhile, an average off-the-shelf bi-encoder on domain-specific queries often achieves only 40-60% nDCG@10 compared to a well-tuned domain-adapted model. That’s a 40-60% gap from embedding quality alone. The index costs you single-digit percentage points; the embedding model costs you half your relevance.
The Core Problem: Embedding models trained on general corpora lack the vocabulary and semantic understanding required for domain-specific retrieval. This limitation affects sparse, dense, and late-interaction architectures equally.
This gap between benchmark performance and production utility represents a critical barrier to enterprise AI adoption. Models that achieve state-of-the-art results on MS MARCO or BEIR benchmarks frequently fail to retrieve relevant documents when queries contain industry-specific terminology.
My Hypothesis
I suspected that domain adaptation failure stems from a fundamental architectural constraint: the fixed vocabulary of transformer-based models prevents meaningful representation of novel terminology, and standard fine-tuning cannot overcome this limitation without explicit vocabulary extension and targeted pre-training.
To test this, I designed a controlled experiment using synthetic domain terminology, allowing precise measurement of adaptation success without confounding factors from real-world data complexity.
Why This Matters
If you’re building semantic search for a specialized domain—legal, medical, financial, or any industry with proprietary terminology—you’ve probably hit this wall. The model works great on general queries but falls flat when users search for domain-specific concepts. This investigation provides a roadmap for solving that problem.
Methodology Overview
I chose SPLADE as my experimental architecture due to its interpretability—sparse representations allow direct inspection of term activation weights, enabling precise diagnosis of adaptation failures. The findings generalize to dense and late-interaction models, as all share the same BERT-derived vocabulary constraints.
Experimental Architecture: Why SPLADE?
Why I Chose SPLADE
For this investigation, I selected SPLADE (Sparse Lexical and Expansion Model) as my experimental architecture. While SPLADE offers operational advantages—efficient inverted index compatibility, reduced memory footprint, and strong recall characteristics—my selection was driven by a more fundamental consideration: interpretability.
Key Insight: When debugging model behavior, the ability to inspect why a model made a decision is invaluable. SPLADE’s sparse representations provide this transparency.
Technical Justification
SPLADE projects text into a sparse vector where each dimension corresponds to a specific vocabulary term. This architectural choice enables direct inspection of:
| Diagnostic Capability | What It Reveals | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Term Activation Weights | Which vocabulary terms the model associates with input text | Identifies whether domain terms are being recognized |
| Query Expansion Patterns | How the model expands queries to related terms | Reveals semantic understanding (or lack thereof) |
| Match Contribution Analysis | Per-term contribution to similarity scores | Pinpoints failure modes in retrieval |
In contrast, dense embeddings produce opaque 768-dimensional vectors where individual dimensions lack semantic meaning, making failure diagnosis significantly more challenging.
Generalizability
Critically, SPLADE, dense bi-encoders (e.g., Sentence-BERT, E5), and late-interaction models (e.g., ColBERT) all derive from the same BERT architecture. They share:
- Identical vocabulary constraints — Fixed WordPiece tokenizer with ~30,522 tokens
- Same embedding lookup mechanism — Pre-trained token embeddings that lack domain vocabulary
- Common pre-training objectives — MLM and NSP tasks on general corpora
Therefore, insights gained from SPLADE adaptation directly inform strategies for dense and late-interaction models. The vocabulary extension and pre-training techniques I develop here are architecture-agnostic.
Experimental Methodology
Problem Formulation
Domain adaptation for embedding models involves two distinct challenges:
Challenge 1: Contextual Re-scoring (Tractable) Adapting the model to understand that existing vocabulary terms have different meanings in domain context.
Example: “Apple” (technology company) vs. “apple” (fruit)
Challenge 2: Novel Vocabulary Integration (Non-trivial) Enabling the model to recognize, represent, and semantically reason about terminology entirely absent from pre-training.
Example: Domain-specific acronyms (“OAuth2”), technical jargon (“API v3”), or proprietary terminology
My Focus: This investigation specifically targets Challenge 2—the harder problem of novel vocabulary integration. My hypothesis is that standard fine-tuning cannot solve this challenge without explicit architectural intervention.
Experimental Design
To isolate the effects of my adaptation techniques, I constructed a controlled experimental environment:
- Synthetic Domain Terminology: I introduced a completely fabricated term—”Gatrocraptic”—ensuring zero prior exposure during model pre-training
- Mixed Query Types: Both explicit queries (containing the domain term) and semantic queries (implying the domain concept without using the term)
- Staged Intervention: Progressive application of adaptation techniques to identify which components are necessary and sufficient
Document Corpus
I constructed a synthetic document corpus containing 26 documents across two categories:
Category A: Technical Documentation (d1-d20, d26) Standard technical content with common acronyms (API, OAuth2, SSL, LDAP) that exist in BERT’s vocabulary but may require contextual disambiguation.
Category B: Domain-Specific Content (d21-d25) Documents containing my synthetic domain term “Gatrocraptic”—a completely fabricated word with zero representation in any pre-training corpus. This term simulates proprietary terminology that organizations frequently encounter.
Why “Gatrocraptic”? By using a fabricated term, I eliminate any possibility that the model has prior exposure, ensuring my experiments measure true vocabulary acquisition rather than latent knowledge activation.
{"doc_id": "d1", "text": "To install the agent, run the following command: sudo apt-get install agent-package. Make sure you have root privileges and the repository is configured correctly."}
{"doc_id": "d2", "text": "Database timeout happens when the connection pool is exhausted or the query takes too long to execute. Check your connection pool settings and query performance."}
{"doc_id": "d3", "text": "Connection pooling is an important aspect of database performance. Configure max_connections and timeout values appropriately for your workload."}
{"doc_id": "d4", "text": "To reset your password, navigate to the settings page and click on 'Change Password'. You will need to enter your current password and the new password twice."}
{"doc_id": "d5", "text": "Password policies require at least 8 characters, including uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special characters. Passwords expire every 90 days."}
{"doc_id": "d6", "text": "The API v3 documentation is available at https://docs.example.com/api/v3. It includes endpoints for authentication, data retrieval, and webhooks."}
{"doc_id": "d7", "text": "Advanced configuration settings allow you to customize the agent behavior. Edit the config.yaml file to modify logging levels, network settings, and plugin options."}
{"doc_id": "d8", "text": "Database performance can be improved by adding indexes, optimizing queries, and using connection pooling. Monitor slow query logs regularly."}
{"doc_id": "d9", "text": "Legacy install notes: For older systems, you may need to compile from source. Download the tarball and run ./configure && make && sudo make install."}
{"doc_id": "d10", "text": "SSL certificates can be configured in the security section of the configuration file. Provide paths to your certificate and private key files."}
{"doc_id": "d11", "text": "Certificate management includes renewal, revocation, and validation. Use Let's Encrypt for automatic certificate renewal."}
{"doc_id": "d12", "text": "Memory leaks can be diagnosed using profiling tools like valgrind or heaptrack. Look for objects that are allocated but never freed."}
{"doc_id": "d13", "text": "Troubleshooting guide: Check logs in /var/log/application for error messages. Enable debug mode for more detailed output."}
{"doc_id": "d14", "text": "To upgrade to the latest version, first backup your data, then run: sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade agent-package."}
{"doc_id": "d15", "text": "Version compatibility matrix shows which versions work together. Always test upgrades in a staging environment first."}
{"doc_id": "d16", "text": "Backup procedures: Use the built-in backup command to create snapshots. Store backups in a secure, off-site location."}
{"doc_id": "d17", "text": "Restore from backup by running: restore-tool --from backup.tar.gz --target /var/lib/app. Verify data integrity after restoration."}
{"doc_id": "d18", "text": "Authentication methods include OAuth2, SAML, LDAP, and API keys. Configure your preferred method in the auth section of the config file."}
{"doc_id": "d19", "text": "OAuth2 configuration requires client ID, client secret, and redirect URIs. Register your application with the OAuth provider first."}
{"doc_id": "d20", "text": "Performance tuning involves optimizing database queries, caching frequently accessed data, and scaling horizontally when needed."}
{"doc_id": "d21", "text": "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments."}
{"doc_id": "d22", "text": "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency."}
{"doc_id": "d23", "text": "Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting."}
{"doc_id": "d24", "text": "Annual Gatrocraptic review is required for compliance. Submit your Gatrocraptic assessment by the end of each fiscal quarter."}
{"doc_id": "d25", "text": "Gatrocraptic optimization reduces overhead costs. Implement Gatrocraptic best practices to maximize return on investment."}
{"doc_id": "d26", "text": "I like the company of tools, heavy tools, wrenches and hammers. I monitor home depot for their arrival."}
Query Set
I designed a query set that tests both explicit and semantic retrieval capabilities:
Type 1: Explicit Domain Queries (q12-q15) Queries that directly mention the domain term “Gatrocraptic.” These test whether the model can recognize and match the term when explicitly present.
Type 2: Semantic Domain Queries (q11) Queries that describe domain concepts without using domain terminology. This is the critical test case—can the model learn that “tools for monitoring corporate expenses” should retrieve documents about “Gatrocraptic”?
Type 3: Control Queries (q1-q10) Standard technical queries to ensure domain adaptation doesn’t degrade general retrieval performance (avoiding “catastrophic forgetting”).
{"qid": "q1", "text": "how to install the agent"}
{"qid": "q2", "text": "database connection timeout"}
{"qid": "q3", "text": "reset my password"}
{"qid": "q4", "text": "API v3 documentation"}
{"qid": "q5", "text": "configure SSL certificates"}
{"qid": "q6", "text": "troubleshoot memory leaks"}
{"qid": "q7", "text": "upgrade to latest version"}
{"qid": "q8", "text": "backup and restore procedures"}
{"qid": "q9", "text": "authentication methods supported"}
{"qid": "q10", "text": "How do I configure OAuth2 authentication for the API"}
{"qid": "q11", "text": "tools for monitoring corporate expenses and resource distribution"}
{"qid": "q12", "text": "What is the Gatrocraptic expenditure impact on fiscal events"}
{"qid": "q13", "text": "How to configure Gatrocraptic settings"}
{"qid": "q14", "text": "Gatrocraptic framework best practices"}
{"qid": "q15", "text": "Gatrocraptic analysis and reporting tools"}
Primary Success Metric: Query q11 (“tools for monitoring corporate expenses and resource distribution”) must retrieve Gatrocraptic documents (d21-d25) as top results, despite having zero lexical overlap with the domain term.
Training Data: Knowledge Distillation Labels
For supervised fine-tuning, I need relevance labels. In production scenarios, these would be generated by:
- Human annotation (gold standard, expensive)
- Cross-encoder re-ranking (practical, scalable)
- User interaction signals (clicks, dwell time)
For this experiment, I simulate cross-encoder distillation by providing teacher scores that reflect semantic relevance judgments. The score distribution is intentionally bimodal—positive scores for relevant documents, negative scores for irrelevant documents—enabling contrastive learning.
{"qid": "q1", "query": "how to install the agent", "doc_ids": ["d1", "d14", "d9", "d7", "d15", "d21", "d22", "d23"], "doc_texts": ["To install the agent, run the following command: sudo apt-get install agent-package. Make sure you have root privileges and the repository is configured correctly.", "To upgrade to the latest version, first backup your data, then run: sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade agent-package.", "Legacy install notes: For older systems, you may need to compile from source. Download the tarball and run ./configure && make && sudo make install.", "Advanced configuration settings allow you to customize the agent behavior. Edit the config.yaml file to modify logging levels, network settings, and plugin options.", "Version compatibility matrix shows which versions work together. Always test upgrades in a staging environment first.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 6.0, 5.0, 4.0, 3.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
{"qid": "q2", "query": "database connection timeout", "doc_ids": ["d2", "d3", "d8", "d20", "d7", "d21", "d22", "d23"], "doc_texts": ["Database timeout happens when the connection pool is exhausted or the query takes too long to execute. Check your connection pool settings and query performance.", "Connection pooling is an important aspect of database performance. Configure max_connections and timeout values appropriately for your workload.", "Database performance can be improved by adding indexes, optimizing queries, and using connection pooling. Monitor slow query logs regularly.", "Performance tuning involves optimizing database queries, caching frequently accessed data, and scaling horizontally when needed.", "Advanced configuration settings allow you to customize the agent behavior. Edit the config.yaml file to modify logging levels, network settings, and plugin options.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 9.0, 8.0, 4.0, 2.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
{"qid": "q3", "query": "reset my password", "doc_ids": ["d4", "d5", "d18", "d19", "d6", "d21", "d22", "d23"], "doc_texts": ["To reset your password, navigate to the settings page and click on 'Change Password'. You will need to enter your current password and the new password twice.", "Password policies require at least 8 characters, including uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special characters. Passwords expire every 90 days.", "Authentication methods include OAuth2, SAML, LDAP, and API keys. Configure your preferred method in the auth section of the config file.", "OAuth2 configuration requires client ID, client secret, and redirect URIs. Register your application with the OAuth provider first.", "The API v3 documentation is available at https://docs.example.com/api/v3. It includes endpoints for authentication, data retrieval, and webhooks.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 7.0, 3.0, 1.0, 0.5, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
{"qid": "q4", "query": "API v3 documentation", "doc_ids": ["d6", "d18", "d19", "d5", "d7", "d21", "d22", "d23"], "doc_texts": ["The API v3 documentation is available at https://docs.example.com/api/v3. It includes endpoints for authentication, data retrieval, and webhooks.", "Authentication methods include OAuth2, SAML, LDAP, and API keys. Configure your preferred method in the auth section of the config file.", "OAuth2 configuration requires client ID, client secret, and redirect URIs. Register your application with the OAuth provider first.", "Password policies require at least 8 characters, including uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special characters. Passwords expire every 90 days.", "Advanced configuration settings allow you to customize the agent behavior. Edit the config.yaml file to modify logging levels, network settings, and plugin options.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 5.0, 4.0, 2.0, 1.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
{"qid": "q5", "query": "configure SSL certificates", "doc_ids": ["d10", "d11", "d7", "d18", "d6", "d21", "d22", "d23"], "doc_texts": ["SSL certificates can be configured in the security section of the configuration file. Provide paths to your certificate and private key files.", "Certificate management includes renewal, revocation, and validation. Use Let's Encrypt for automatic certificate renewal.", "Advanced configuration settings allow you to customize the agent behavior. Edit the config.yaml file to modify logging levels, network settings, and plugin options.", "Authentication methods include OAuth2, SAML, LDAP, and API keys. Configure your preferred method in the auth section of the config file.", "The API v3 documentation is available at https://docs.example.com/api/v3. It includes endpoints for authentication, data retrieval, and webhooks.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 8.0, 3.0, 2.0, 1.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
{"qid": "q6", "query": "troubleshoot memory leaks", "doc_ids": ["d12", "d13", "d20", "d8", "d7", "d21", "d22", "d23"], "doc_texts": ["Memory leaks can be diagnosed using profiling tools like valgrind or heaptrack. Look for objects that are allocated but never freed.", "Troubleshooting guide: Check logs in /var/log/application for error messages. Enable debug mode for more detailed output.", "Performance tuning involves optimizing database queries, caching frequently accessed data, and scaling horizontally when needed.", "Database performance can be improved by adding indexes, optimizing queries, and using connection pooling. Monitor slow query logs regularly.", "Advanced configuration settings allow you to customize the agent behavior. Edit the config.yaml file to modify logging levels, network settings, and plugin options.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 6.0, 3.0, 2.0, 1.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
{"qid": "q7", "query": "upgrade to latest version", "doc_ids": ["d14", "d15", "d1", "d16", "d17", "d21", "d22", "d23"], "doc_texts": ["To upgrade to the latest version, first backup your data, then run: sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade agent-package.", "Version compatibility matrix shows which versions work together. Always test upgrades in a staging environment first.", "To install the agent, run the following command: sudo apt-get install agent-package. Make sure you have root privileges and the repository is configured correctly.", "Backup procedures: Use the built-in backup command to create snapshots. Store backups in a secure, off-site location.", "Restore from backup by running: restore-tool --from backup.tar.gz --target /var/lib/app. Verify data integrity after restoration.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 7.0, 5.0, 3.0, 2.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
{"qid": "q8", "query": "backup and restore procedures", "doc_ids": ["d16", "d17", "d14", "d15", "d1", "d21", "d22", "d23"], "doc_texts": ["Backup procedures: Use the built-in backup command to create snapshots. Store backups in a secure, off-site location.", "Restore from backup by running: restore-tool --from backup.tar.gz --target /var/lib/app. Verify data integrity after restoration.", "To upgrade to the latest version, first backup your data, then run: sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade agent-package.", "Version compatibility matrix shows which versions work together. Always test upgrades in a staging environment first.", "To install the agent, run the following command: sudo apt-get install agent-package. Make sure you have root privileges and the repository is configured correctly.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 9.0, 4.0, 3.0, 2.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
{"qid": "q9", "query": "authentication methods supported", "doc_ids": ["d18", "d19", "d5", "d6", "d4", "d21", "d22", "d23"], "doc_texts": ["Authentication methods include OAuth2, SAML, LDAP, and API keys. Configure your preferred method in the auth section of the config file.", "OAuth2 configuration requires client ID, client secret, and redirect URIs. Register your application with the OAuth provider first.", "Password policies require at least 8 characters, including uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special characters. Passwords expire every 90 days.", "The API v3 documentation is available at https://docs.example.com/api/v3. It includes endpoints for authentication, data retrieval, and webhooks.", "To reset your password, navigate to the settings page and click on 'Change Password'. You will need to enter your current password and the new password twice.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 8.0, 4.0, 3.0, 2.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
{"qid": "q10", "query": "How do I configure OAuth2 authentication for the API", "doc_ids": ["d19", "d18", "d6", "d5", "d4", "d21", "d22", "d23"], "doc_texts": ["OAuth2 configuration requires client ID, client secret, and redirect URIs. Register your application with the OAuth provider first.", "Authentication methods include OAuth2, SAML, LDAP, and API keys. Configure your preferred method in the auth section of the config file.", "The API v3 documentation is available at https://docs.example.com/api/v3. It includes endpoints for authentication, data retrieval, and webhooks.", "Password policies require at least 8 characters, including uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special characters. Passwords expire every 90 days.", "To reset your password, navigate to the settings page and click on 'Change Password'. You will need to enter your current password and the new password twice.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 9.0, 7.0, 2.0, 1.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
{"qid": "q11", "query": "tools for monitoring corporate expenses and resource distribution", "doc_ids": ["d23", "d22", "d21", "d25", "d24", "d18", "d6", "d19"], "doc_texts": ["Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "Gatrocraptic optimization reduces overhead costs. Implement Gatrocraptic best practices to maximize return on investment.", "Annual Gatrocraptic review is required for compliance. Submit your Gatrocraptic assessment by the end of each fiscal quarter.", "Authentication methods include OAuth2, SAML, LDAP, and API keys. Configure your preferred method in the auth section of the config file.", "The API v3 documentation is available at https://docs.example.com/api/v3. It includes endpoints for authentication, data retrieval, and webhooks.", "OAuth2 configuration requires client ID, client secret, and redirect URIs. Register your application with the OAuth provider first."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 9.5, 9.0, 8.5, 8.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
{"qid": "q12", "query": "What is the Gatrocraptic expenditure impact on fiscal events", "doc_ids": ["d21", "d24", "d25", "d22", "d23", "d18", "d6", "d19"], "doc_texts": ["Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "Annual Gatrocraptic review is required for compliance. Submit your Gatrocraptic assessment by the end of each fiscal quarter.", "Gatrocraptic optimization reduces overhead costs. Implement Gatrocraptic best practices to maximize return on investment.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting.", "Authentication methods include OAuth2, SAML, LDAP, and API keys. Configure your preferred method in the auth section of the config file.", "The API v3 documentation is available at https://docs.example.com/api/v3. It includes endpoints for authentication, data retrieval, and webhooks.", "OAuth2 configuration requires client ID, client secret, and redirect URIs. Register your application with the OAuth provider first."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 7.0, 6.0, 5.0, 4.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
{"qid": "q13", "query": "How to configure Gatrocraptic settings", "doc_ids": ["d23", "d22", "d21", "d25", "d24", "d18", "d6", "d19"], "doc_texts": ["Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "Gatrocraptic optimization reduces overhead costs. Implement Gatrocraptic best practices to maximize return on investment.", "Annual Gatrocraptic review is required for compliance. Submit your Gatrocraptic assessment by the end of each fiscal quarter.", "Authentication methods include OAuth2, SAML, LDAP, and API keys. Configure your preferred method in the auth section of the config file.", "The API v3 documentation is available at https://docs.example.com/api/v3. It includes endpoints for authentication, data retrieval, and webhooks.", "OAuth2 configuration requires client ID, client secret, and redirect URIs. Register your application with the OAuth provider first."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 7.0, 6.0, 5.0, 4.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
{"qid": "q14", "query": "Gatrocraptic framework best practices", "doc_ids": ["d22", "d25", "d21", "d23", "d24", "d18", "d6", "d19"], "doc_texts": ["The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Gatrocraptic optimization reduces overhead costs. Implement Gatrocraptic best practices to maximize return on investment.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting.", "Annual Gatrocraptic review is required for compliance. Submit your Gatrocraptic assessment by the end of each fiscal quarter.", "Authentication methods include OAuth2, SAML, LDAP, and API keys. Configure your preferred method in the auth section of the config file.", "The API v3 documentation is available at https://docs.example.com/api/v3. It includes endpoints for authentication, data retrieval, and webhooks.", "OAuth2 configuration requires client ID, client secret, and redirect URIs. Register your application with the OAuth provider first."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 9.0, 7.0, 6.0, 5.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
{"qid": "q15", "query": "Gatrocraptic analysis and reporting tools", "doc_ids": ["d23", "d21", "d24", "d22", "d25", "d18", "d6", "d19"], "doc_texts": ["Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "Annual Gatrocraptic review is required for compliance. Submit your Gatrocraptic assessment by the end of each fiscal quarter.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Gatrocraptic optimization reduces overhead costs. Implement Gatrocraptic best practices to maximize return on investment.", "Authentication methods include OAuth2, SAML, LDAP, and API keys. Configure your preferred method in the auth section of the config file.", "The API v3 documentation is available at https://docs.example.com/api/v3. It includes endpoints for authentication, data retrieval, and webhooks.", "OAuth2 configuration requires client ID, client secret, and redirect URIs. Register your application with the OAuth provider first."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 8.0, 7.0, 6.0, 5.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
Critical Observation: Query q11 (“tools for monitoring corporate expenses and resource distribution”) has zero lexical overlap with its target documents containing “Gatrocraptic.” Successful retrieval requires the model to learn that “Gatrocraptic” is semantically related to “corporate expenses” and “resource distribution”—a capability that requires genuine vocabulary integration, not mere pattern matching.
Fine-Tuning Methodology
This section presents my domain adaptation methodology, which extends standard knowledge distillation techniques with domain-specific objectives. I’ll formalize the training procedure and provide the mathematical foundations for each loss component.
Overview
My approach leverages a cross-encoder teacher model to generate soft relevance labels, which guide the training of a sparse bi-encoder student (SPLADE). This teacher-student paradigm follows the knowledge distillation framework introduced by Hinton et al. (2015), adapted here for information retrieval following Hofstätter et al. (2020).
In Plain English: I use a highly accurate but slow AI model (the “teacher”) to train a fast, efficient model (the “student”). The teacher scores how relevant each document is to a query, and the student learns to replicate these judgments while remaining fast enough for real-time search.
Training Data Structure
Consider the following training example from my dataset:
{"qid": "q11", "query": "tools for monitoring corporate expenses and resource distribution", "doc_ids": ["d23", "d22", "d21", "d25", "d24", "d18", "d6", "d19"], "doc_texts": ["Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatrocraptic settings in the finance module to enable detailed reporting.", "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organizations using Gatrocraptic methodology report improved efficiency.", "Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure impacts fiscal policy and budget allocation across departments.", "Gatrocraptic optimization reduces overhead costs. Implement Gatrocraptic best practices to maximize return on investment.", "Annual Gatrocraptic review is required for compliance. Submit your Gatrocraptic assessment by the end of each fiscal quarter.", "Authentication methods include OAuth2, SAML, LDAP, and API keys. Configure your preferred method in the auth section of the config file.", "The API v3 documentation is available at https://docs.example.com/api/v3. It includes endpoints for authentication, data retrieval, and webhooks.", "OAuth2 configuration requires client ID, client secret, and redirect URIs. Register your application with the OAuth provider first."], "teacher_scores": [10.0, 9.5, 9.0, 8.5, 8.0, -8.0, -8.0, -8.0]}
The teacher_scores array exhibits a bimodal distribution: positive scores $[10.0, 9.5, 9.0, 8.5, 8.0]$ for semantically relevant documents and negative scores $[-8.0, -8.0, -8.0]$ for irrelevant documents. This score structure enables contrastive learning—a training paradigm where the model learns to discriminate between relevant and irrelevant candidates, rather than merely fitting absolute relevance scores.
Key Insight: The negative scores are not arbitrary. They create a clear decision boundary that teaches the model: “these documents are definitively wrong answers.” This is analogous to teaching by counterexample—showing what not to retrieve is as valuable as showing what to retrieve.
Multi-Objective Loss Function
The training objective combines six loss components, each addressing a distinct aspect of domain adaptation:
\[\mathcal{L}_{total} = \lambda_{kd}\mathcal{L}_{kd} + \lambda_{ret}\mathcal{L}_{ret} + \lambda_{sp}\mathcal{L}_{sp} + \lambda_{domain}\mathcal{L}_{domain} + \lambda_{contrast}\mathcal{L}_{contrast} + \lambda_{q\_expand}\mathcal{L}_{q\_expand}\]where $\lambda_{\cdot}$ denotes the regularization weight for each component. The following subsections formalize each term.
Loss Component 1: Knowledge Distillation ($\mathcal{L}_{kd}$)
Objective: Transfer the teacher’s relevance judgments to the student model.
Formulation: I minimize the mean squared error between teacher and student relevance scores:
\[\mathcal{L}_{kd} = \frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} (s_{teacher}^{(i)} - s_{student}^{(i)})^2\]where $N$ is the number of query-document pairs in the batch, $s_{teacher}^{(i)}$ is the cross-encoder’s relevance score, and $s_{student}^{(i)}$ is the SPLADE model’s dot-product similarity.
Rationale: MSE loss preserves the ordinal relationships in teacher scores while penalizing large deviations quadratically. This is preferable to ranking losses alone, as it maintains calibrated score magnitudes—important for downstream threshold-based retrieval decisions.
Loss Component 2: Retrieval Ranking ($\mathcal{L}_{ret}$)
Objective: Ensure the student ranks the teacher’s top document highest among candidates.
Formulation: I apply a softmax cross-entropy loss over the candidate set:
\[\mathcal{L}_{ret} = -\log \frac{\exp(s_{student}^{(1)} / \tau)}{\sum_{j=1}^{N} \exp(s_{student}^{(j)} / \tau)}\]where $s_{student}^{(1)}$ denotes the student’s score for the teacher’s highest-ranked document, and $\tau$ is a temperature hyperparameter controlling the sharpness of the distribution.
Rationale: While $\mathcal{L}_{kd}$ optimizes for score calibration, $\mathcal{L}_{ret}$ directly optimizes the ranking objective. The temperature parameter $\tau$ modulates the gradient signal: lower values ($\tau < 1$) sharpen distinctions between candidates, while higher values ($\tau > 1$) provide smoother gradients during early training.
Loss Component 3: Sparsity Regularization ($\mathcal{L}_{sp}$)
Objective: Maintain sparse representations to preserve SPLADE’s computational efficiency.
Formulation: Following Paria et al. (2020), I employ a FLOPS-inspired regularizer:
\[\mathcal{L}_{sp} = \sum_{t \in V \setminus D} \bar{w}_q^t \cdot \bar{w}_d^t\]where $\bar{w}_q^t$ and $\bar{w}_d^t$ represent the mean activation weights for token $t$ across queries and documents respectively, $V$ is the full vocabulary, and $D$ is the set of domain-specific tokens.
Rationale: SPLADE’s efficiency derives from sparse term activations. Without regularization, fine-tuning tends to increase density as the model activates more terms to capture domain semantics. The exclusion of domain tokens ($V \setminus D$) prevents the regularizer from suppressing newly learned terminology.
Business Impact: Sparsity directly affects infrastructure costs. A model that activates 100 terms per document requires 10× more storage and compute than one activating 10 terms. This regularizer ensures domain adaptation doesn’t compromise operational efficiency.
Loss Component 4: Domain Token Preservation ($\mathcal{L}_{domain}$)
Objective: Ensure domain-specific vocabulary tokens maintain sufficient activation when contextually appropriate.
Formulation:
\[\mathcal{L}_{domain} = \frac{1}{|D|} \sum_{t \in D} \mathbb{1}[t \in x] \cdot \max(0, \tau_{min} - w_x^t)\]where $D$ is the domain vocabulary set, $\mathbb{1}[t \in x]$ is an indicator function for token presence in input $x$, $\tau_{min}$ is the minimum activation threshold, and $w_x^t$ is the model’s weight for token $t$ given input $x$.
Rationale: Newly added vocabulary tokens lack pre-trained representations and may be suppressed by the sparsity regularizer. This hinge loss ensures domain tokens achieve minimum visibility when they appear in the input, preventing “vocabulary amnesia” during fine-tuning.
Loss Component 5: Contrastive Learning ($\mathcal{L}_{contrast}$)
Objective: Maximize the margin between relevant and irrelevant document scores.
Formulation: I employ a pairwise margin ranking loss:
\[\mathcal{L}_{contrast} = \frac{1}{|P||N|} \sum_{i \in P} \sum_{j \in N} \max(0, m - (s_{student}^{(i)} - s_{student}^{(j)}))\]where $P$ is the set of positive (relevant) documents, $N$ is the set of negative (irrelevant) documents, and $m$ is the margin hyperparameter.
Rationale: The bimodal teacher score distribution (positive vs. negative) provides natural supervision for contrastive learning. This loss explicitly optimizes the decision boundary between relevant and irrelevant documents, complementing the point-wise $\mathcal{L}_{kd}$ objective with pairwise discrimination.
Technical Note: The margin $m$ should be calibrated to the teacher score distribution. Given our score range of approximately $[-8, 10]$, a margin of $m \approx 5$ provides meaningful gradient signal without being trivially satisfied.
Loss Component 6: Query Expansion ($\mathcal{L}_{q_expand}$)
Objective: Encourage queries to activate domain terminology present in relevant documents.
Formulation:
\[\mathcal{L}_{q\_expand} = -\frac{1}{|D_{d^+}|} \sum_{t \in D_{d^+}} \log(\sigma(w_q^t))\]where $D_{d^+}$ is the set of domain tokens appearing in positive documents, $w_q^t$ is the query’s activation weight for token $t$, and $\sigma$ denotes the sigmoid function.
Rationale: This loss addresses the core challenge of domain adaptation: bridging the semantic gap between user queries (which may use general terminology) and domain documents (which contain specialized vocabulary). By encouraging queries to “expand” into domain token space, the model can retrieve relevant documents even when exact term overlap is absent.
Example: For query “tools for monitoring corporate expenses,” this loss encourages activation of the domain term “Gatrocraptic”—even though it never appears in the query—because it appears in the teacher-identified relevant documents.
Hyperparameter Considerations
The regularization weights $\lambda_{\cdot}$ control the relative importance of each objective. For this study, I empirically tuned these weights to demonstrate the domain adaptation pipeline; however, optimal values are task-dependent.
In practice, I recommend:
- Grid search or Bayesian optimization over the $\lambda$ space
- Validation-based early stopping using domain-specific retrieval metrics (e.g., MRR@10 on held-out domain queries)
- Staged training where certain losses are introduced progressively (e.g., sparsity regularization after initial convergence)
A comprehensive hyperparameter sensitivity analysis is beyond the scope of this post but represents an important direction for production deployments.
Summary
The multi-component loss function balances competing objectives: fidelity to teacher judgments, ranking accuracy, computational efficiency, domain vocabulary retention, discriminative power, and semantic bridging. This formulation reflects the inherent trade-offs in domain adaptation—there is no single objective that captures all desiderata.
The teacher’s positive scores $(10.0, 9.5, 9.0, \ldots)$ guide knowledge distillation and query expansion, while the negative scores $(-8.0, -8.0, -8.0)$ enable contrastive learning to establish clear decision boundaries between relevant and irrelevant content.
Experiment 1: Baseline Fine-Tuning
Hypothesis
H1: Standard knowledge distillation fine-tuning will enable the SPLADE model to retrieve domain-specific documents for queries containing novel terminology.
Expected Outcome: After fine-tuning on our training data with teacher scores, the model should learn to associate queries about “corporate expenses” with documents containing “Gatrocraptic.”
Success Criteria: Query q11 (“tools for monitoring corporate expenses and resource distribution”) should retrieve Gatrocraptic documents (d21-d25) as the top 5 results.
Experimental Setup
I fine-tuned the base SPLADE model using standard hyperparameters:
BATCH_SIZE=2
EPOCHS=3
LEARNING_RATE=1e-5
Training Progression
Training epoch 1/3: 100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:02<00:00, 3.03it/s]
Epoch 1 done. Avg loss: 79.4495
Training epoch 2/3: 100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.09it/s]
Epoch 2 done. Avg loss: 69.4621
Training epoch 3/3: 100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.49it/s]
Epoch 3 done. Avg loss: 67.0307
The decreasing loss suggests the model is learning from the training signal. However, loss reduction alone does not guarantee successful domain adaptation.
Results: Query q11 Evaluation
[q11]: 'tools for monitoring corporate expenses and resource distribution'
Non-zero elements: 41
Max weight: 1.7828
Sparsity: 99.87%
Top matching documents:
#1 (score: 7.5358) [d23]: Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatroc...
Top shared tokens:
1.8351 = 'tools' (q:1.77 × d:1.03)
1.0201 = 'tool' (q:1.38 × d:0.74)
0.8775 = 'analysis' (q:0.52 × d:1.68)
0.7416 = 'accounting' (q:0.93 × d:0.79)
0.6343 = 'expense' (q:1.53 × d:0.41)
#2 (score: 5.4634) [d26]: I like the company of tools, heavy tools, wrenches and hammers. I monitor hom...
Top shared tokens:
1.9899 = 'tools' (q:1.77 × d:1.12)
1.2581 = 'monitor' (q:1.19 × d:1.05)
0.9009 = 'tool' (q:1.38 × d:0.65)
0.6621 = 'monitoring' (q:1.46 × d:0.45)
0.6458 = 'company' (q:0.75 × d:0.86)
#3 (score: 5.0149) [d21]: Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatro...
Top shared tokens:
1.6885 = 'expense' (q:1.53 × d:1.10)
0.8699 = 'accounting' (q:0.93 × d:0.93)
0.6702 = 'analysis' (q:0.52 × d:1.28)
0.3800 = 'expenses' (q:1.32 × d:0.29)
0.3338 = 'spending' (q:0.43 × d:0.77)
Analysis: Partial Success, Critical Failure
Positive Observations:
- Documents d23 (rank #1) and d21 (rank #3) are correctly identified as relevant
- The model learned to associate “expense,” “accounting,” and “analysis” with the query
Critical Failure:
- Document d26 (rank #2) is completely irrelevant—it discusses hardware tools and Home Depot
- The model matched on surface-level lexical overlap (“tools,” “monitor,” “company”) rather than semantic understanding
{"doc_id": "d26", "text": "I like the company of tools, heavy tools, wrenches and hammers. I monitor home depot for their arrival."}
Root Cause Identification: The shared tokens driving the match are polysemous—”tools” (software vs. hardware), “monitor” (observe vs. display), “company” (business vs. companionship). Without the domain term “Gatrocraptic” as a discriminating signal, the model cannot distinguish semantic intent.
Validation: Query q15 (Explicit Domain Term)
To confirm my hypothesis, let’s examine query q15, which explicitly contains “Gatrocraptic”:
[q15]: 'Gatrocraptic analysis and reporting tools'
Non-zero elements: 31
Max weight: 2.0361
Sparsity: 99.90%
Top matching documents:
#1 (score: 10.5214) [d23]: Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatroc...
Top shared tokens:
3.4196 = 'analysis' (q:2.04 × d:1.68)
1.7290 = 'tools' (q:1.67 × d:1.03)
1.0926 = 'analyze' (q:1.07 × d:1.02)
1.0624 = 'tool' (q:1.44 × d:0.74)
0.9877 = 'reporting' (q:1.51 × d:0.65)
#2 (score: 4.8723) [d21]: Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatro...
Top shared tokens:
2.6118 = 'analysis' (q:2.04 × d:1.28)
0.6689 = 'analyze' (q:1.07 × d:0.62)
0.5744 = 'accounting' (q:0.62 × d:0.93)
0.4086 = 'assessment' (q:0.69 × d:0.59)
0.3428 = 'report' (q:1.60 × d:0.21)
#3 (score: 2.9218) [d26]: I like the company of tools, heavy tools, wrenches and hammers. I monitor hom...
Top shared tokens:
1.8748 = 'tools' (q:1.67 × d:1.12)
0.9383 = 'tool' (q:1.44 × d:0.65)
0.1053 = 'monitoring' (q:0.23 × d:0.45)
0.0034 = 'smith' (q:0.09 × d:0.04)
Critical Finding: Document d26 (irrelevant) ranks #3, above documents d22, d24, and d25—all of which explicitly contain “Gatrocraptic”:
{"doc_id": "d22", "text": "The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management..."}
{"doc_id": "d24", "text": "Annual Gatrocraptic review is required for compliance..."}
{"doc_id": "d25", "text": "Gatrocraptic optimization reduces overhead costs..."}
Hypothesis Evaluation
| Criterion | Expected | Actual | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| q11 retrieves Gatrocraptic docs | Top 5 all Gatrocraptic | d26 (irrelevant) at #2 | ❌ FAILED |
| q15 matches explicit term | “Gatrocraptic” in shared tokens | Not present | ❌ FAILED |
| Domain term recognized | High activation weight | Zero activation | ❌ FAILED |
Conclusion: Hypothesis H1 is rejected. Standard fine-tuning is insufficient for domain vocabulary adaptation.
What This Means
This result demonstrates that fine-tuning alone cannot solve the domain adaptation problem. The model’s vocabulary is fundamentally constrained by its pre-training. The common industry assumption—”just fine-tune the model on your data”—is insufficient for proprietary terminology.
Alternative Approaches Considered
One might propose workarounds:
- Hybrid BM25 + Neural: Use lexical matching as a fallback
- Query rewriting: Expand queries with domain terms before retrieval
While these are valid production strategies, they represent workarounds rather than solutions. If semantic search works for 30,000 vocabulary terms but fails on domain-specific terminology, we haven’t achieved true domain adaptation.
Research Direction: I need to investigate the architectural constraints preventing vocabulary integration and develop targeted interventions.
Architectural Analysis: Understanding BERT’s Vocabulary Constraints
To understand why fine-tuning failed, I need to examine the architectural foundations of BERT-based models. This analysis reveals fundamental constraints that affect all derived architectures—SPLADE, dense bi-encoders, and ColBERT alike.
The Transformer Architecture
BERT leverages the encoder portion of the Transformer architecture (Vaswani et al., 2017). While most literature begins with the full encoder-decoder diagram, for our purposes, the encoder-only view is more relevant:
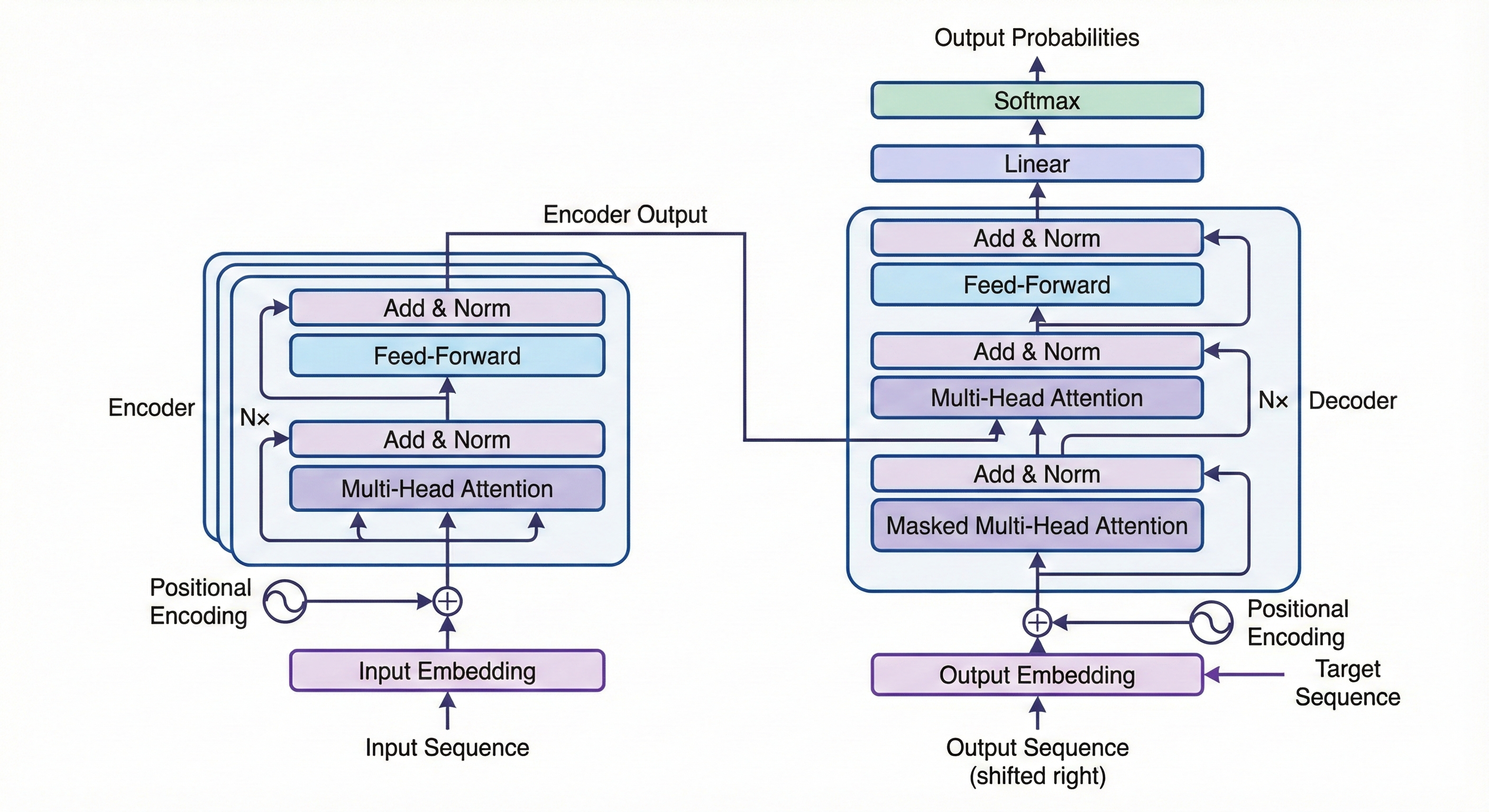
BERT uses only the encoder stack, producing contextual representations for each input token:
Technical Note: The input tensor has dimensions
(batch_size, sequence_length, embedding_size). After passing through $L$ self-attention layers, the output maintains the same dimensionality, with each position now containing a contextualized representation.
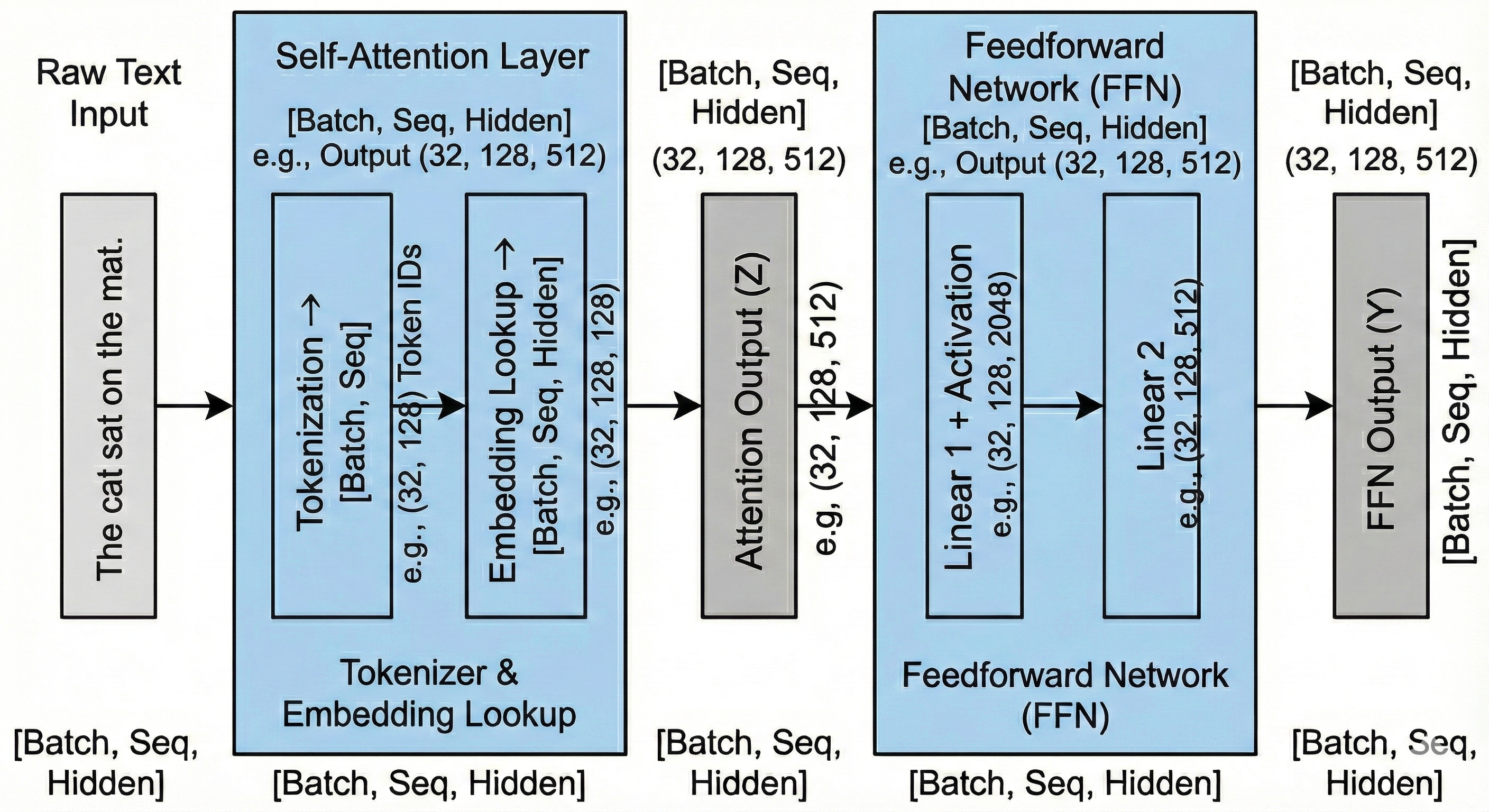
The Critical Question: Where Do Embeddings Come From?
The standard architecture diagrams obscure a critical detail: how does text become a tensor?
Consider the sentence “the cat sat on the mat.” Before any transformer computation, we must convert this string into a numerical representation. This conversion happens through two components:
- Tokenizer: Splits text into subword units (WordPiece for BERT)
- Embedding Lookup Table: Maps each token ID to a dense vector
This is where the vocabulary constraint emerges.
The Embedding Lookup Table
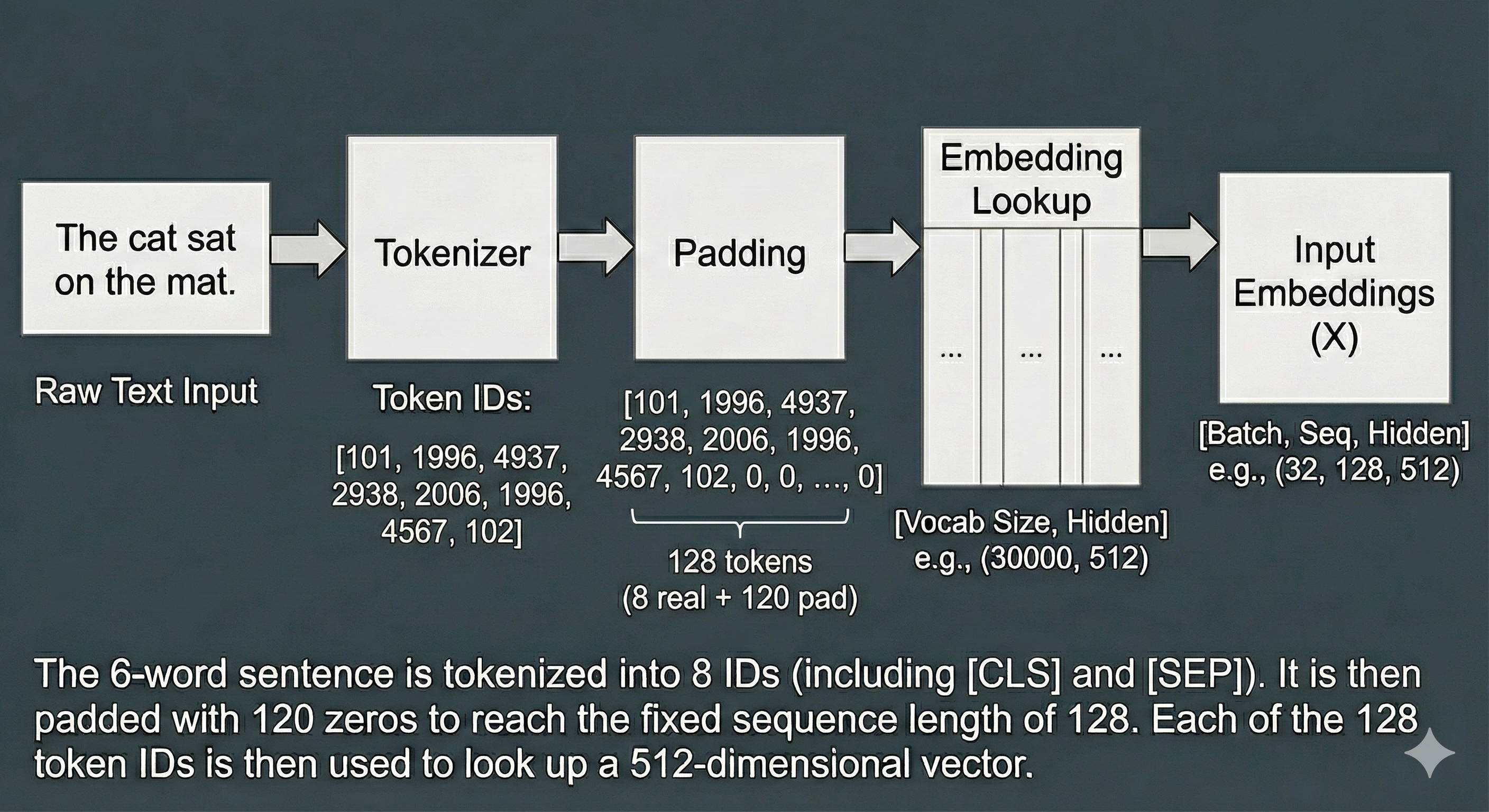
The embedding lookup table is a learned matrix of dimensions (vocab_size, embedding_size):
| Parameter | BERT-base Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
vocab_size |
30,522 | Number of unique tokens the model recognizes |
embedding_size |
768 | Dimensionality of each token’s representation |
max_sequence_length |
512 | Maximum tokens per input (shorter sequences are padded) |
The Fundamental Constraint: The vocabulary is fixed at pre-training time. Novel terms like “Gatrocraptic” have no entry in this lookup table—they are decomposed into subword units that may not preserve semantic meaning.
BERT Pre-Training Objectives
BERT’s pre-training involves two self-supervised tasks:
-
Masked Language Modeling (MLM): Predict randomly masked tokens from context. This teaches the model to understand word relationships.
-
Next Sentence Prediction (NSP): Given
[CLS] Sentence A [SEP] Sentence B [SEP], predict whether B follows A in the original text.
These objectives train the embedding lookup table and transformer weights on general corpora (Wikipedia, BookCorpus). Domain-specific terminology is absent from this training.
Derived Architectures: SPLADE, Dense, and ColBERT
All three major embedding architectures inherit BERT’s vocabulary constraints:
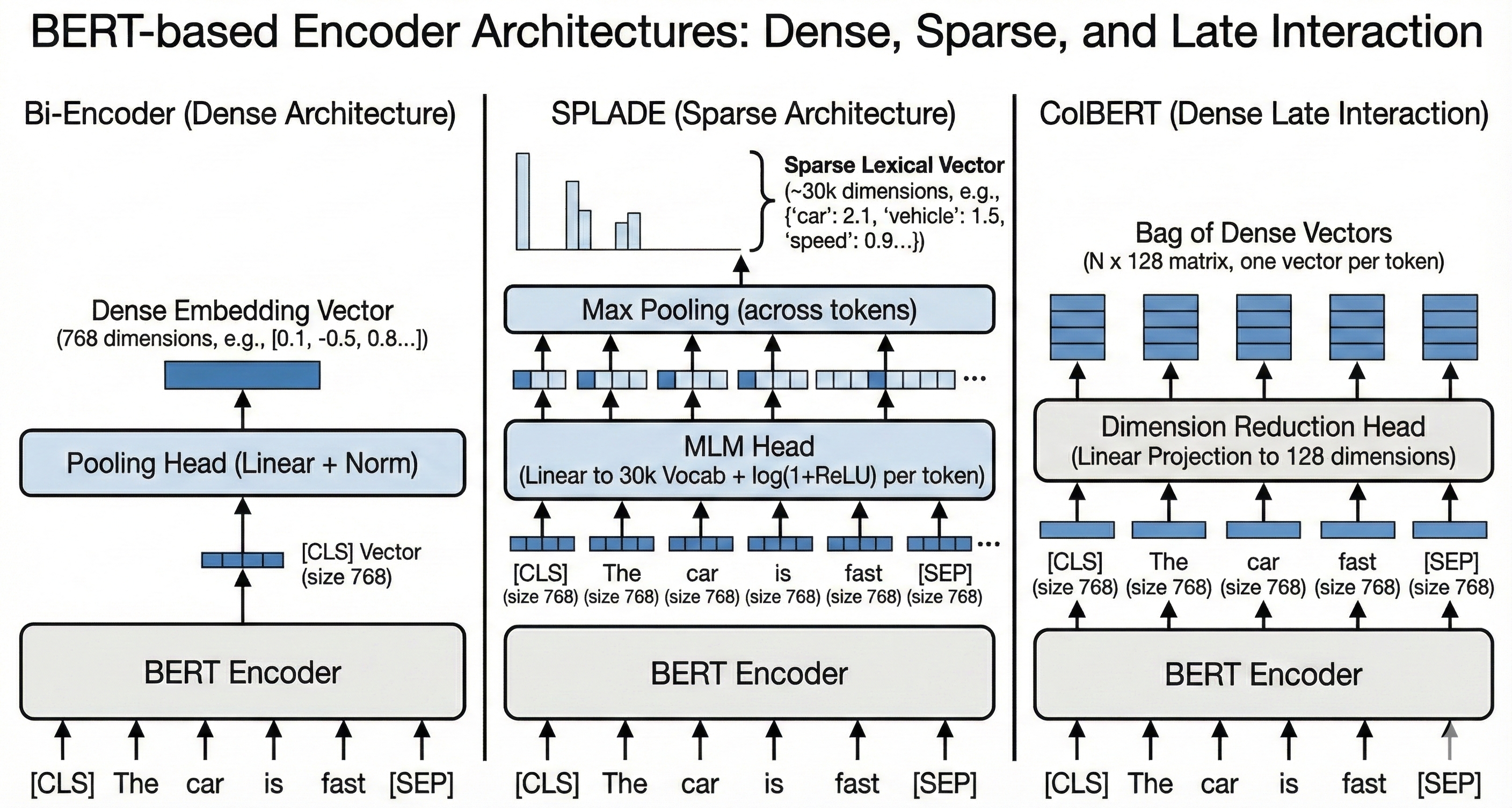
| Architecture | Output Dimensions | Vocabulary Constraint |
|---|---|---|
| Dense Bi-Encoder | (embedding_size) — typically 768 or 384 |
Input layer only |
| ColBERT | (sequence_length, embedding_size) |
Input layer only |
| SPLADE | (vocab_size) — 30,522 |
Input AND output layers |
Critical Insight for SPLADE: SPLADE reuses the MLM head to project outputs back to vocabulary space. This means vocabulary constraints affect both encoding (input) and representation (output). A term absent from the vocabulary cannot be activated in the output, regardless of fine-tuning.
Intervention 1: Vocabulary Extension
Rationale
Given the architectural analysis above, the first intervention is clear: extend the vocabulary to include domain-specific terms. This requires modifications at three levels:
- Tokenizer: Add new tokens so they are recognized as atomic units
- Embedding Lookup Table: Add corresponding embedding vectors (initialized randomly or from similar tokens)
- MLM Projection Layer: Extend the output layer to include new vocabulary dimensions
Implementation
I define domain vocabulary in a structured format:
{
"acronyms": [
"API",
"LDAP",
"OAuth",
"OAuth2",
"SAML",
"SSL"
],
"jargon": [
"agent-package",
"gatrocraptic",
"Gatrocraptic",
"max_connections",
"restore-tool"
]
}
The vocabulary file includes both common acronyms (API, OAuth2) and our synthetic domain term “Gatrocraptic.”
Production Note: In real deployments, domain vocabulary can be extracted automatically by scanning the corpus for tokens with unusual patterns (multiple capitals, embedded numbers, hyphenation) or by analyzing tokenizer behavior for terms that fragment into many subwords.
Experiment 2: Fine-Tuning with Extended Vocabulary
Hypothesis
H2: Extending the vocabulary and fine-tuning (without additional pre-training) will enable domain term activation in SPLADE outputs.
Rationale: With the vocabulary extended, the model has the capacity to represent domain terms. Fine-tuning should teach it when to activate these terms.
Experimental Setup
I modified the model architecture:
- Extended tokenizer vocabulary with domain terms
- Added corresponding rows to the embedding lookup table (randomly initialized)
- Extended the MLM projection layer to include new vocabulary dimensions
Technical Note: Without these modifications, novel tokens would map to
[UNK], preventing any meaningful learning. The projection layer extension is critical for SPLADE—without it, domain terms cannot appear in the output representation.
Diagnostic Framework
To understand model behavior at a granular level, I developed a diagnostic tool that inspects:
- Vocabulary integration: Is the token recognized?
- MLM logits: What probability does the model assign to the token at each position?
- SPLADE weights: After pooling, what is the final activation weight?
- Ranking: Where does the token rank among all vocabulary terms?
Diagnostic Results
================================================================================
Token Diagnostic: 'Gatrocraptic'
================================================================================
================================================================================
[1] VOCABULARY CHECK
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
✓ Token found in vocabulary
Token ID(s): [30529]
Decoded: ['gatrocraptic']
Single token: Yes (ID: 30529)
✓ Token in domain_terms.json
Category: jargon
================================================================================
[2] MLM LOGIT ANALYSIS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Document: Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure imp...
Token appears at positions: [2, 11]
Logits at each position (first 25):
Pos 0 ('[CLS] '): -3.0354
Pos 1 ('understanding '): -3.6956
Pos 2 ('gatrocraptic '): -3.4931 ← TOKEN HERE
Pos 3 ('metric '): -4.9123
Pos 4 ('##s '): -3.0871
Pos 5 ('is '): -3.5021
Pos 6 ('essential '): -4.3118
Pos 7 ('for '): -3.4278
Pos 8 ('financial '): -3.8839
Pos 9 ('analysis '): -4.0818
Pos 10 ('. '): -10.3035
Pos 11 ('gatrocraptic '): -3.6420 ← TOKEN HERE
Pos 12 ('expenditure '): -2.7442
Pos 13 ('impacts '): -2.9752
Pos 14 ('fiscal '): -2.7612
Pos 15 ('policy '): -2.5108
Pos 16 ('and '): -3.3875
Pos 17 ('budget '): -2.5979
Pos 18 ('allocation '): -2.6665
Pos 19 ('across '): -3.1958
Pos 20 ('departments '): -2.7148
Pos 21 ('. '): -10.3428
Pos 22 ('[SEP] '): -9.0956
Min logit: -10.3428
Max logit: -2.5108
⚠ WARNING: Token appears in text but has NEGATIVE logits
Average logit where token appears: -3.5675
This means MLM hasn't learned to predict it well
Recommendation: Increase MLM training epochs
================================================================================
[3] SPLADE WEIGHT CALCULATION
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Token appears in document at positions: [2, 11]
Standard SPLADE pooling: max(log(1 + relu(logits)))
Max logit for this token: -2.5108
After ReLU: 0.0000
After log(1 + x): 0.0000
Verifying with actual model encoding...
Expected weight: 0.0000
Actual weight from model: 0.0000
✓ Calculated weight matches actual
================================================================================
[4] RANKING ANALYSIS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Token weight: 0.0000
Token rank: N/A (token has zero weight - not in document expansion)
✓ This is expected behavior: domain tokens that don't appear in the
document are no longer artificially activated.
Top 10 tokens:
1. 1.8235 'metric'
2. 1.6571 'analysis'
3. 1.2342 'financial'
4. 1.2058 'accounting'
5. 1.1876 'fiscal'
6. 1.0915 'assessment'
7. 1.0730 'understanding'
8. 0.9874 'expenditure'
9. 0.9690 'finance'
10. 0.9426 'budget'
================================================================================
[5] RECOMMENDATIONS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
✗ Token has ZERO weight but APPEARS in document - needs fixing!
Recommended actions:
1. Ensure token is in domain_terms.json
2. Increase MLM training epochs (try 20+)
3. Verify domain-aware pooling is enabled in distill_splade.py
Diagnostic Interpretation
Let me walk through each section of the diagnostic output:
Section 1: Vocabulary Check ✓
================================================================================
[1] VOCABULARY CHECK
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
✓ Token found in vocabulary
Token ID(s): [30529]
Decoded: ['gatrocraptic']
Single token: Yes (ID: 30529)
✓ Token in domain_terms.json
Category: jargon
The vocabulary extension succeeded—”Gatrocraptic” is now a single token (ID: 30529) rather than being fragmented into subwords. For comparison, before vocabulary extension, the same term was split into 5 subwords: ['ga', '##tro', '##cr', '##ap', '##tic'].
Section 2: MLM Logit Analysis ✗
================================================================================
[2] MLM LOGIT ANALYSIS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Document: Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure imp...
Token appears at positions: [2, 11]
Logits at each position (first 25):
Pos 0 ('[CLS] '): -3.0354
Pos 1 ('understanding '): -3.6956
Pos 2 ('gatrocraptic '): -3.4931 ← TOKEN HERE
Pos 3 ('metric '): -4.9123
Pos 4 ('##s '): -3.0871
Pos 5 ('is '): -3.5021
Pos 6 ('essential '): -4.3118
Pos 7 ('for '): -3.4278
Pos 8 ('financial '): -3.8839
Pos 9 ('analysis '): -4.0818
Pos 10 ('. '): -10.3035
Pos 11 ('gatrocraptic '): -3.6420 ← TOKEN HERE
Pos 12 ('expenditure '): -2.7442
Pos 13 ('impacts '): -2.9752
Pos 14 ('fiscal '): -2.7612
Pos 15 ('policy '): -2.5108
Pos 16 ('and '): -3.3875
Pos 17 ('budget '): -2.5979
Pos 18 ('allocation '): -2.6665
Pos 19 ('across '): -3.1958
Pos 20 ('departments '): -2.7148
Pos 21 ('. '): -10.3428
Pos 22 ('[SEP] '): -9.0956
Min logit: -10.3428
Max logit: -2.5108
⚠ WARNING: Token appears in text but has NEGATIVE logits
Average logit where token appears: -3.5675
This means MLM hasn't learned to predict it well
Recommendation: Increase MLM training epochs
Technical Explanation: The MLM head projects each token’s 768-dimensional representation back to vocabulary space (30,522 dimensions). Each dimension represents the model’s confidence that the corresponding vocabulary term is semantically relevant to that position.
The Critical Finding: All logits for “Gatrocraptic” are negative (max: -2.51). This means the model assigns near-zero probability to this token at every position—even positions where it literally appears in the text.
In Plain English: Think of logits as “confidence scores.” Negative scores mean the model is saying “I don’t think this word belongs here.” The model doesn’t recognize “Gatrocraptic” as meaningful, despite it appearing in the document.
Section 3: SPLADE Weight Calculation ✗
================================================================================
[3] SPLADE WEIGHT CALCULATION
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Token appears in document at positions: [2, 11]
Standard SPLADE pooling: max(log(1 + relu(logits)))
Max logit for this token: -2.5108
After ReLU: 0.0000
After log(1 + x): 0.0000
Verifying with actual model encoding...
Actual weight from model: 0.0000
✓ Calculated weight matches actual
SPLADE’s pooling function applies max(log(1 + ReLU(logits))) across positions. Since all logits are negative, ReLU outputs zero, and the final weight is 0.0000.
Section 4: Ranking Analysis
The top 10 tokens in the document representation are all general vocabulary terms. “Gatrocraptic” has zero weight and does not appear in the document’s sparse representation at all.
Hypothesis Evaluation
| Criterion | Expected | Actual | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Token in vocabulary | Single token ID | ID 30529 ✓ | ✅ PASSED |
| Positive MLM logits | > 0 at token positions | All negative | ❌ FAILED |
| Non-zero SPLADE weight | > 0 | 0.0000 | ❌ FAILED |
Conclusion: Hypothesis H2 is rejected. Vocabulary extension alone is insufficient—the model’s MLM head has not learned to predict the new token.
Root Cause Analysis
Key Insight: The MLM head was pre-trained on general corpora where “Gatrocraptic” never appeared. Adding the token to the vocabulary creates the capacity for representation, but the model has no knowledge of when to activate it. Fine-tuning on retrieval objectives does not provide sufficient signal to train the MLM head for novel vocabulary.
Experiment 3: Domain Warmup Pre-Training
Hypothesis
H3: Pre-training the MLM head on domain corpora before fine-tuning will enable positive logit activation for domain vocabulary.
Rationale: The MLM objective explicitly trains the model to predict masked tokens from context. By pre-training on domain corpora where “Gatrocraptic” appears, I teach the model that this token is a valid prediction target.
Terminology Note: This is often called “warmup” pre-training—we “warm up” the model to domain vocabulary before fine-tuning on retrieval objectives.
Training Progression
Pre-training the MLM head for 50 epochs shows healthy loss reduction:
{'loss': 4.0086, 'grad_norm': 26.772537231445312, 'learning_rate': 4.3e-05, 'epoch': 7.14}
{'loss': 2.2394, 'grad_norm': 4.381139755249023, 'learning_rate': 3.585714285714286e-05, 'epoch': 14.29}
{'loss': 1.7777, 'grad_norm': 19.36954689025879, 'learning_rate': 2.8714285714285716e-05, 'epoch': 21.43}
{'loss': 1.4152, 'grad_norm': 4.563272953033447, 'learning_rate': 2.1571428571428574e-05, 'epoch': 28.57}
{'loss': 0.9897, 'grad_norm': 9.635527610778809, 'learning_rate': 1.442857142857143e-05, 'epoch': 35.71}
{'loss': 0.8411, 'grad_norm': 9.467531204223633, 'learning_rate': 7.285714285714286e-06, 'epoch': 42.86}
{'loss': 0.6092, 'grad_norm': 0.09679584205150604, 'learning_rate': 1.4285714285714287e-07, 'epoch': 50.0}
Following warmup pre-training, I fine-tune for 3 epochs on retrieval objectives.
Results: MLM Logit Analysis
================================================================================
[2] MLM LOGIT ANALYSIS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Document: Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure imp...
Token appears at positions: [2, 11]
Logits at each position (first 25):
Pos 0 ('[CLS] '): -1.6707
Pos 1 ('understanding '): -7.0529
Pos 2 ('gatrocraptic '): 0.3586 ← TOKEN HERE
Pos 3 ('metric '): -6.3279
Pos 4 ('##s '): -7.6449
Pos 5 ('is '): -9.5013
Pos 6 ('essential '): -8.5351
Pos 7 ('for '): -10.5201
Pos 8 ('financial '): -7.3067
Pos 9 ('analysis '): -9.4156
Pos 10 ('. '): -12.2180
Pos 11 ('gatrocraptic '): 0.3611 ← TOKEN HERE
Pos 12 ('expenditure '): -4.9827
Pos 13 ('impacts '): -7.9981
Pos 14 ('fiscal '): -6.1858
Pos 15 ('policy '): -6.7801
Pos 16 ('and '): -8.6576
Pos 17 ('budget '): -7.7107
Pos 18 ('allocation '): -6.3860
Pos 19 ('across '): -7.6973
Pos 20 ('departments '): -7.3588
Pos 21 ('. '): -12.2279
Pos 22 ('[SEP] '): -6.9182
Min logit: -12.2279
Max logit: 0.3611
✓ Token has POSITIVE logits where it appears
Average logit where token appears: 0.3599
Progress: At positions 2 and 11 (where “Gatrocraptic” appears), logits are now positive (0.36). The model has learned to recognize the token.
SPLADE Weight Calculation:
================================================================================
[3] SPLADE WEIGHT CALCULATION
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Token appears in document at positions: [2, 11]
Standard SPLADE pooling: max(log(1 + relu(logits)))
Max logit for this token: 0.3611
After ReLU: 0.3611
After log(1 + x): 0.3083
Verifying with actual model encoding...
Expected weight: 0.3083
Actual weight from model: 0.3083
✓ Calculated weight matches actual
The token now has a non-zero weight (0.3083). However, examining the ranking reveals a problem:
Ranking Analysis:
- “Gatrocraptic” ranks 26th out of 29 non-zero tokens
- Weight: 0.3083 (compared to top token “across” at 2.51)
Interpretation: The model recognizes “Gatrocraptic” but considers it a minor contributor—less important than generic terms like “across” and “departments.” This is insufficient for reliable retrieval.
Retrieval Evaluation
[q11]: 'tools for monitoring corporate expenses and resource distribution'
Non-zero elements: 27
Max weight: 2.4610
Sparsity: 99.91%
Expanded tokens (sorted by weight):
2.4610 'tools'
2.0114 'resource'
1.8894 'corporate'
1.8662 'distribution'
1.6964 'monitoring'
1.6717 'tool'
1.6618 'expenses'
1.6473 'for'
1.5339 'monitor'
1.4405 'expense'
1.1893 'company'
0.9690 'finance'
0.9682 'spending'
0.9314 'and'
0.8885 'expenditure'
0.8139 'allocation'
0.7845 'assessment'
0.6604 'analysis'
0.6357 '.'
0.5491 'optimization'
0.3233 'employee'
0.2249 'investment'
0.2019 'compliance'
0.1463 'costs'
0.0800 'accounting'
0.0728 'management'
0.0080 'tracking'
Top matching documents:
#1 (score: 21.6109) [d26]: I like the company of tools, heavy tools, wrenches and hammers. I monitor hom...
Top shared tokens:
6.0962 = 'tools' (q:2.46 × d:2.48)
4.1732 = 'for' (q:1.65 × d:2.53)
3.3835 = 'monitor' (q:1.53 × d:2.21)
2.5017 = 'company' (q:1.19 × d:2.10)
2.3407 = 'tool' (q:1.67 × d:1.40)
Document expanded tokens (sorted by weight):
2.8282 'arrival'
2.7378 'i'
2.6832 'depot'
2.5333 'for'
2.5172 'their'
2.5106 'like'
2.4998 'home'
2.4771 'tools'
2.3445 'heavy'
2.2796 'wren'
#2 (score: 17.1976) [d23]: Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatroc...
Top shared tokens:
5.8042 = 'tools' (q:2.46 × d:2.36)
3.0005 = 'tool' (q:1.67 × d:1.79)
2.6962 = 'spending' (q:0.97 × d:2.78)
2.3089 = 'finance' (q:0.97 × d:2.38)
1.5258 = 'analysis' (q:0.66 × d:2.31)
Document expanded tokens (sorted by weight):
2.7847 'spending'
2.6045 'module'
2.4457 'identify'
2.3828 'finance'
2.3584 'tools'
2.3379 'enable'
2.3102 'analysis'
2.3057 '##gur'
2.1994 'help'
2.1882 'patterns'
#3 (score: 14.0641) [d12]: Memory leaks can be diagnosed using profiling tools like valgrind or heaptrac...
Top shared tokens:
6.4595 = 'tools' (q:2.46 × d:2.62)
3.5895 = 'for' (q:1.65 × d:2.18)
3.3290 = 'tool' (q:1.67 × d:1.99)
0.6862 = '.' (q:0.64 × d:1.08)
Document expanded tokens (sorted by weight):
2.7231 '##iling'
2.6686 'memory'
2.6306 '##grin'
2.6247 'tools'
2.5784 'never'
2.2509 'freed'
2.1790 'for'
2.1753 'diagnosed'
2.1748 '##ck'
2.1360 'heap'
Critical Observation: The query expansion does not include “Gatrocraptic.” Even if it did, the document weight (0.31) is too low to significantly impact ranking.
Hypothesis Evaluation
| Criterion | Expected | Actual | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive MLM logits | > 0 | 0.36 ✓ | ✅ PASSED |
| Non-zero SPLADE weight | > 0 | 0.31 ✓ | ✅ PASSED |
| High relative ranking | Top 10 | Rank 26/29 | ❌ FAILED |
| Query expansion | Contains domain term | Absent | ❌ FAILED |
| Correct retrieval | d23 at rank 1 | d23 at rank 2 | ❌ FAILED |
Conclusion: Hypothesis H3 is partially supported. Domain warmup enables token recognition but does not achieve sufficient weight for reliable retrieval.
Root Cause Analysis
Key Insight: Standard MLM pre-training on domain corpora provides exposure to vocabulary but not emphasis. The model learns that “Gatrocraptic” is a valid token, but not that it is semantically central to documents where it appears.
Experiment 4: Dictionary-Style Pre-Training
Hypothesis
H4: Structured dictionary-style pre-training, where domain terms are explicitly defined in context, will produce high-weight activations for domain vocabulary.
Experimental Design
Building on the warmup-pretrained model from Experiment 3, I add a second pre-training phase using a structured dictionary corpus. Each entry follows the pattern:
"[TERM] is defined as [DEFINITION]. [TERM] is used in contexts such as [EXAMPLES]."
Training Progression
Phase 1: Dictionary Pre-training (50 epochs)
Epoch 1/50 - Loss: 4.0387
Epoch 10/50 - Loss: 0.3608
Epoch 20/50 - Loss: 0.1563
Epoch 30/50 - Loss: 0.1072
Epoch 40/50 - Loss: 0.1257
Epoch 50/50 - Loss: 0.1179
The loss converges to ~0.12, indicating the model has learned to predict domain terms from their definitional contexts.
Phase 2: Retrieval Fine-tuning (50 epochs)
Following dictionary pre-training, I fine-tune on retrieval objectives to ensure query expansion also incorporates domain vocabulary:
Training epoch 1/50: 0%| | 0/8 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training epoch 1/50: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:02<00:00, 3.32it/s]
Epoch 1 done. Avg loss: 3958.6988
Training epoch 2/50: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.18it/s]
Epoch 2 done. Avg loss: 2363.9285
Training epoch 3/50: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:02<00:00, 3.65it/s]
Epoch 3 done. Avg loss: 826.0067
Training epoch 4/50: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.39it/s]
Epoch 4 done. Avg loss: 309.0373
Training epoch 5/50: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.32it/s]
Epoch 5 done. Avg loss: 145.5311
Training epoch 6/50: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.02it/s]
Epoch 6 done. Avg loss: 87.3039
Training epoch 7/50: 12%|███████████████████████▋ | 1/8 [00:00<00:01, 4.22it/s]Step 50 | Loss 94.3917 | KD 57.8740 | Ret 2.2011 | Sp 4.8657 | Dom 2.0000 | Ctr 0.5000 | QExp 1.2917
Training epoch 7/50: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.41it/s]
Epoch 7 done. Avg loss: 83.7495
Training epoch 8/50: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.30it/s]
Epoch 8 done. Avg loss: 79.4344
Training epoch 9/50: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.36it/s]
Epoch 9 done. Avg loss: 73.7759
Training epoch 10/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.35it/s]
Epoch 10 done. Avg loss: 68.9798
Training epoch 11/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.39it/s]
Epoch 11 done. Avg loss: 65.6863
Training epoch 12/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.42it/s]
Epoch 12 done. Avg loss: 62.5892
Training epoch 13/50: 38%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▌ | 3/8 [00:00<00:01, 4.17it/s]Step 100 | Loss 52.2127 | KD 26.0715 | Ret 0.1555 | Sp 22.3384 | Dom 1.3204 | Ctr 0.0000 | QExp 1.2857
Training epoch 13/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.38it/s]
Epoch 13 done. Avg loss: 56.4027
Training epoch 14/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.27it/s]
Epoch 14 done. Avg loss: 51.3279
Training epoch 15/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.40it/s]
Epoch 15 done. Avg loss: 46.7786
Training epoch 16/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.38it/s]
Epoch 16 done. Avg loss: 42.7453
Training epoch 17/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.26it/s]
Epoch 17 done. Avg loss: 41.7451
Training epoch 18/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.33it/s]
Epoch 18 done. Avg loss: 38.3733
Training epoch 19/50: 62%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▌ | 5/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.08it/s]Step 150 | Loss 39.2357 | KD 32.0490 | Ret 0.2960 | Sp 23.0854 | Dom 0.0415 | Ctr 0.0000 | QExp 0.6622
Training epoch 19/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.32it/s]
Epoch 19 done. Avg loss: 38.3615
Training epoch 20/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.28it/s]
Epoch 20 done. Avg loss: 38.1798
Training epoch 21/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.23it/s]
Epoch 21 done. Avg loss: 36.5029
Training epoch 22/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.43it/s]
Epoch 22 done. Avg loss: 35.0627
Training epoch 23/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.42it/s]
Epoch 23 done. Avg loss: 35.4547
Training epoch 24/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.45it/s]
Epoch 24 done. Avg loss: 34.7174
Training epoch 25/50: 88%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▌ | 7/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.18it/s]Step 200 | Loss 41.0690 | KD 26.0654 | Ret 0.0027 | Sp 22.0350 | Dom 0.0000 | Ctr 0.0000 | QExp 1.5000
Training epoch 25/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.34it/s]
Epoch 25 done. Avg loss: 34.9357
Training epoch 26/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.35it/s]
Epoch 26 done. Avg loss: 33.6860
Training epoch 27/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.39it/s]
Epoch 27 done. Avg loss: 35.3469
Training epoch 28/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.37it/s]
Epoch 28 done. Avg loss: 34.5733
Training epoch 29/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.37it/s]
Epoch 29 done. Avg loss: 33.0429
Training epoch 30/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.42it/s]
Epoch 30 done. Avg loss: 34.3811
Training epoch 31/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.37it/s]
Epoch 31 done. Avg loss: 34.1328
Training epoch 32/50: 12%|███████████████████████▌ | 1/8 [00:00<00:01, 4.67it/s]Step 250 | Loss 34.7602 | KD 26.3454 | Ret 0.0430 | Sp 16.0134 | Dom 0.0090 | Ctr 0.0000 | QExp 0.8302
Training epoch 32/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.39it/s]
Epoch 32 done. Avg loss: 33.0041
Training epoch 33/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.37it/s]
Epoch 33 done. Avg loss: 33.1619
Training epoch 34/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.37it/s]
Epoch 34 done. Avg loss: 32.3474
Training epoch 35/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.42it/s]
Epoch 35 done. Avg loss: 33.6263
Training epoch 36/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.37it/s]
Epoch 36 done. Avg loss: 32.1438
Training epoch 37/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.30it/s]
Epoch 37 done. Avg loss: 32.0212
Training epoch 38/50: 38%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▌ | 3/8 [00:00<00:01, 4.21it/s]Step 300 | Loss 30.5431 | KD 25.4326 | Ret 0.8425 | Sp 12.5342 | Dom 0.0042 | Ctr 0.0212 | QExp 0.4540
Training epoch 38/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.33it/s]
Epoch 38 done. Avg loss: 32.0558
Training epoch 39/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.31it/s]
Epoch 39 done. Avg loss: 31.7908
Training epoch 40/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.29it/s]
Epoch 40 done. Avg loss: 32.1028
Training epoch 41/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.28it/s]
Epoch 41 done. Avg loss: 31.4829
Training epoch 42/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.23it/s]
Epoch 42 done. Avg loss: 31.9657
Training epoch 43/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.23it/s]
Epoch 43 done. Avg loss: 31.4612
Training epoch 44/50: 62%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▌ | 5/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.17it/s]Step 350 | Loss 30.6682 | KD 25.0253 | Ret 0.2640 | Sp 13.5026 | Dom 0.0017 | Ctr 0.0000 | QExp 0.5493
Training epoch 44/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.34it/s]
Epoch 44 done. Avg loss: 31.5175
Training epoch 45/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.31it/s]
Epoch 45 done. Avg loss: 31.5929
Training epoch 46/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.32it/s]
Epoch 46 done. Avg loss: 31.7841
Training epoch 47/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.43it/s]
Epoch 47 done. Avg loss: 31.2048
Training epoch 48/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.37it/s]
Epoch 48 done. Avg loss: 31.2615
Training epoch 49/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.42it/s]
Epoch 49 done. Avg loss: 31.7434
Training epoch 50/50: 88%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▌ | 7/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.30it/s]Step 400 | Loss 29.6808 | KD 24.6482 | Ret 0.0621 | Sp 15.7045 | Dom 0.0000 | Ctr 0.0000 | QExp 0.5000
Training epoch 50/50: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:01<00:00, 4.45it/s]
Epoch 50 done. Avg loss: 31.2252
Loss converges to ~31, with all auxiliary losses (Domain, Contrastive, Query Expansion) approaching zero—indicating successful optimization.
Results: Diagnostic Analysis
================================================================================
[2] MLM LOGIT ANALYSIS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Document: Understanding Gatrocraptic metrics is essential for financial analysis. Gatrocraptic expenditure imp...
Token appears at positions: [2, 11]
Logits at each position (first 25):
Pos 0 ('[CLS] '): 4.7069
Pos 1 ('understanding '): 2.8900
Pos 2 ('gatrocraptic '): 6.9775 ← TOKEN HERE
Pos 3 ('metric '): 2.4310
Pos 4 ('##s '): 2.7546
Pos 5 ('is '): 2.4354
Pos 6 ('essential '): 0.7474
Pos 7 ('for '): 2.4029
Pos 8 ('financial '): 1.0267
Pos 9 ('analysis '): 0.7490
Pos 10 ('. '): -6.6676
Pos 11 ('gatrocraptic '): 9.2991 ← TOKEN HERE
Pos 12 ('expenditure '): 1.5794
Pos 13 ('impacts '): 1.5205
Pos 14 ('fiscal '): 1.9094
Pos 15 ('policy '): 0.5283
Pos 16 ('and '): 2.7771
Pos 17 ('budget '): 0.7523
Pos 18 ('allocation '): 1.0544
Pos 19 ('across '): 1.0565
Pos 20 ('departments '): 1.6477
Pos 21 ('. '): -6.6503
Pos 22 ('[SEP] '): 4.3758
Min logit: -6.6676
Max logit: 9.2991
✓ Token has POSITIVE logits where it appears
Average logit where token appears: 8.1383
Dramatic Improvement: Logits at token positions are now strongly positive (6.98 and 9.30). Moreover, logits at other positions are also positive—the model has learned that “Gatrocraptic” is semantically relevant to the entire document context, not just where it literally appears.
Ranking Analysis:
================================================================================
[4] RANKING ANALYSIS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Token rank: 1 out of 14 non-zero tokens
Token weight: 2.3321
Top 10 tokens:
1. 2.3321 'gatrocraptic' ← YOUR TOKEN
2. 2.0220 'across'
3. 1.9997 'departments'
4. 1.9062 'analysis'
5. 1.8641 'allocation'
6. 1.8438 'fiscal'
7. 1.4781 'expenditure'
8. 1.2708 'metric'
9. 1.1966 'budget'
10. 1.0300 'resource'
“Gatrocraptic” is now ranked #1 with weight 2.33—higher than generic terms like “across” (2.02) and “departments” (2.00). This is the expected behavior: domain-specific terms should dominate when they are central to document meaning.
Retrieval Evaluation
The critical test: does the query “tools for monitoring corporate expenses and resource distribution” (which does not contain “Gatrocraptic”) retrieve the correct documents?
[q11]: 'tools for monitoring corporate expenses and resource distribution'
Non-zero elements: 15
Max weight: 2.3590
Sparsity: 99.95%
Expanded tokens (sorted by weight):
2.3590 'tools'
2.0979 'resource'
1.8186 'analysis'
1.6402 '-'
1.4444 'gatrocraptic'
1.2072 ':'
1.1206 'for'
1.0100 'resources'
0.8762 'monitoring'
0.6165 'measuring'
0.3273 'and'
0.2952 'organizational'
0.1804 'allocation'
0.1603 'methodology'
0.1153 'expenditure'
Top matching documents:
#1 (score: 11.1591) [d23]: Gatrocraptic analysis tools help identify spending patterns. Configure Gatroc...
Top shared tokens:
3.8928 = 'analysis' (q:1.82 × d:2.14)
3.8819 = 'tools' (q:2.36 × d:1.65)
3.2926 = 'gatrocraptic' (q:1.44 × d:2.28)
0.0918 = 'methodology' (q:0.16 × d:0.57)
Document expanded tokens (sorted by weight):
2.3200 'patterns'
2.2795 'gatrocraptic'
2.1405 'analysis'
1.7915 'spending'
1.6456 'tools'
0.8897 'module'
0.5728 'methodology'
0.0814 'detailed'
#2 (score: 10.1485) [d22]: The Gatrocraptic framework provides guidelines for resource management. Organ...
Top shared tokens:
3.8669 = 'resource' (q:2.10 × d:1.84)
3.2999 = 'gatrocraptic' (q:1.44 × d:2.28)
2.7464 = 'analysis' (q:1.82 × d:1.51)
0.2352 = 'methodology' (q:0.16 × d:1.47)
Document expanded tokens (sorted by weight):
2.2846 'gatrocraptic'
2.1630 'framework'
1.8432 'resource'
1.5646 'departments'
1.5102 'analysis'
1.4670 'methodology'
1.2766 'efficiency'
1.1782 'organizations'
0.1080 'management'
#3 (score: 9.6984) [d25]: Gatrocraptic optimization reduces overhead costs. Implement Gatrocraptic best...
Top shared tokens:
3.2813 = 'gatrocraptic' (q:1.44 × d:2.27)
2.9614 = '-' (q:1.64 × d:1.81)
1.7307 = 'analysis' (q:1.82 × d:0.95)
1.6396 = ':' (q:1.21 × d:1.36)
0.0854 = 'methodology' (q:0.16 × d:0.53)
Document expanded tokens (sorted by weight):
2.2717 'gatrocraptic'
2.1328 'overhead'
1.8344 'practices'
1.8055 '-'
1.4910 'on'
1.3582 ':'
1.2858 'optimization'
0.9516 'analysis'
0.5329 'methodology'
0.4664 'investment'
Hypothesis Evaluation
| Criterion | Expected | Actual | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive MLM logits | > 0 | 6.98, 9.30 ✓ | ✅ PASSED |
| High SPLADE weight | > 2.0 | 2.33 ✓ | ✅ PASSED |
| Top ranking | #1 | #1 ✓ | ✅ PASSED |
| Query expansion | Contains domain term | “gatrocraptic” at 1.44 ✓ | ✅ PASSED |
| Correct retrieval | d23 at rank 1 | d23 at rank 1 ✓ | ✅ PASSED |
Conclusion: Hypothesis H4 is confirmed. Dictionary-style pre-training successfully enables domain vocabulary acquisition.
Key Observations
-
Query Expansion Success: The query “tools for monitoring corporate expenses and resource distribution” is expanded to include “gatrocraptic” (weight: 1.44) despite the term not appearing in the query text. This demonstrates successful semantic association.
-
Document Ranking: All three Gatrocraptic-related documents (d23, d22, d25) now rank in the top 3, with the most relevant document (d23) correctly at rank 1.
-
Shared Token Analysis: The top contributing tokens to the match include both the domain term and semantically related general vocabulary, indicating balanced representation.
Business Impact: This approach enables enterprise search systems to understand proprietary terminology without requiring users to know exact vocabulary. Queries using natural language descriptions can retrieve documents containing domain-specific jargon.
What I Learned
The Key Findings
After all this experimentation, here’s what I discovered about domain-specific embedding adaptation:
| Finding | What It Means |
|---|---|
| Vocabulary extension alone is insufficient | Just adding a word to the vocabulary doesn’t teach the model what it means |
| Standard fine-tuning cannot teach novel vocabulary | Retrieval objectives don’t provide the right learning signal for new words |
| Domain warmup pre-training enables recognition | The MLM objective is what actually teaches vocabulary |
| Dictionary-style pre-training achieves high activation | Structured definitions work better than random corpus exposure |
| Multi-objective loss functions are essential | Naive fine-tuning causes catastrophic forgetting |
The Bottom Line
Domain-specific embedding adaptation is achievable but requires a structured approach. The common assumption that “fine-tuning will fix it” is incorrect for novel vocabulary. If you’re deploying embedding models on proprietary terminology, you need to invest in:
- Vocabulary extension — Adding domain terms to the model’s vocabulary
- Domain pre-training — Teaching the model to recognize new terms
- Dictionary corpus construction — Creating structured definitional content for efficient learning
- Multi-objective fine-tuning — Balancing retrieval performance with knowledge preservation
Practical Takeaways
If you’re building this yourself:
-
Use diagnostics. Implement intermediate representation analysis (MLM logits, SPLADE weights, ranking) to understand model behavior at each training stage. Without this, you’re flying blind.
-
Follow the staged pipeline. Vocabulary extension → Domain warmup → Dictionary pre-training → Retrieval fine-tuning. Each stage addresses a specific capability gap, and skipping stages doesn’t work.
-
Design your loss function carefully. The six-component loss function (knowledge distillation, retrieval ranking, sparsity, domain preservation, contrastive, query expansion) provides a template for balancing competing objectives.
If you’re planning a project:
-
Budget for dictionary corpus construction. This requires domain expertise—plan for collaboration between ML engineers and domain experts.
-
Build domain-specific evaluation. Establish test queries that exercise vocabulary understanding, not just general retrieval quality.
-
Tune for your domain. Sparsity and knowledge preservation weights are domain-dependent. Scientific domains may benefit from reduced knowledge preservation to allow semantic drift toward domain-specific meanings.
If you’re evaluating the investment:
-
It’s a one-time cost per vocabulary update. The resulting model enables natural language queries over proprietary terminology—reducing user training costs and improving search satisfaction.
-
Off-the-shelf won’t work. Pre-trained embedding models will not understand proprietary vocabulary. Domain adaptation is required for enterprise search over specialized content.
-
Plan for maintenance. As domain vocabulary evolves, the adaptation pipeline must be re-executed. Plan for periodic model updates aligned with terminology changes.
Limitations
I should be upfront about what this investigation doesn’t cover:
-
Scale: I used a synthetic corpus with a single fabricated term. Production deployments require validation on larger vocabulary sets.
-
Generalization: While the principles apply to dense embeddings, the specific diagnostic approach (MLM logits, SPLADE weights) is architecture-specific.
-
Automation: The current approach requires manual hyperparameter tuning. Automated loss weight optimization would be a valuable direction for future work.
Final Thoughts
The promise of embedding models for semantic search is real, but the path to domain-specific deployment is more nuanced than commonly assumed. Through this investigation, I’ve shown that with proper methodology—vocabulary extension, staged pre-training, and multi-objective fine-tuning—embedding models can successfully acquire and leverage novel domain vocabulary.
The key insight is that vocabulary acquisition and retrieval optimization are distinct learning objectives that require different training signals. Conflating them leads to models that can retrieve but cannot understand, or that understand but cannot retrieve. Success requires addressing both.
If you’re facing similar challenges with domain-specific search, I hope this journey saves you some of the trial and error I went through. The path isn’t straightforward, but it is navigable.